Anyone who intentionally or by mistake does not pay the amount to the state can face serious tax evasion penalties. Being a Houston resident, you don’t expect problems when starting a business or filing a return. Understanding general IRS guidelines and how penalties are applied can help clarify how enforcement decisions are evaluated.
A mistake can happen from a person, but there is a difference between an intentional act and doing it unknowingly, which is important to realize. This article outlines factors to consider when differentiating between intentional and unintentional errors.
What May Count as Tax Evasion
When a person deliberately tries to ignore the tax amount, it is counted as tax evasion. From an IRS standpoint, intent separates errors from enforcement actions.
When intent is found behind the act, an individual may face tax evasion penalties that may even result in criminal exposure, including potential imprisonment.
How are Tax Evasion Penalties Different From Other IRS Penalties
All penalties are not the same. IRS first looks into the root to find whether it was willful, oversight, or unknown to decide the penalty. For example, late payment penalties are relatively common and, in some cases, may be eligible for abatement depending on the facts.
But when it comes to intentional acts, the fine amount may increase along with increased chances of criminal prosecution in some cases.
What are the Most Common Penalties Tied to Tax Evasion
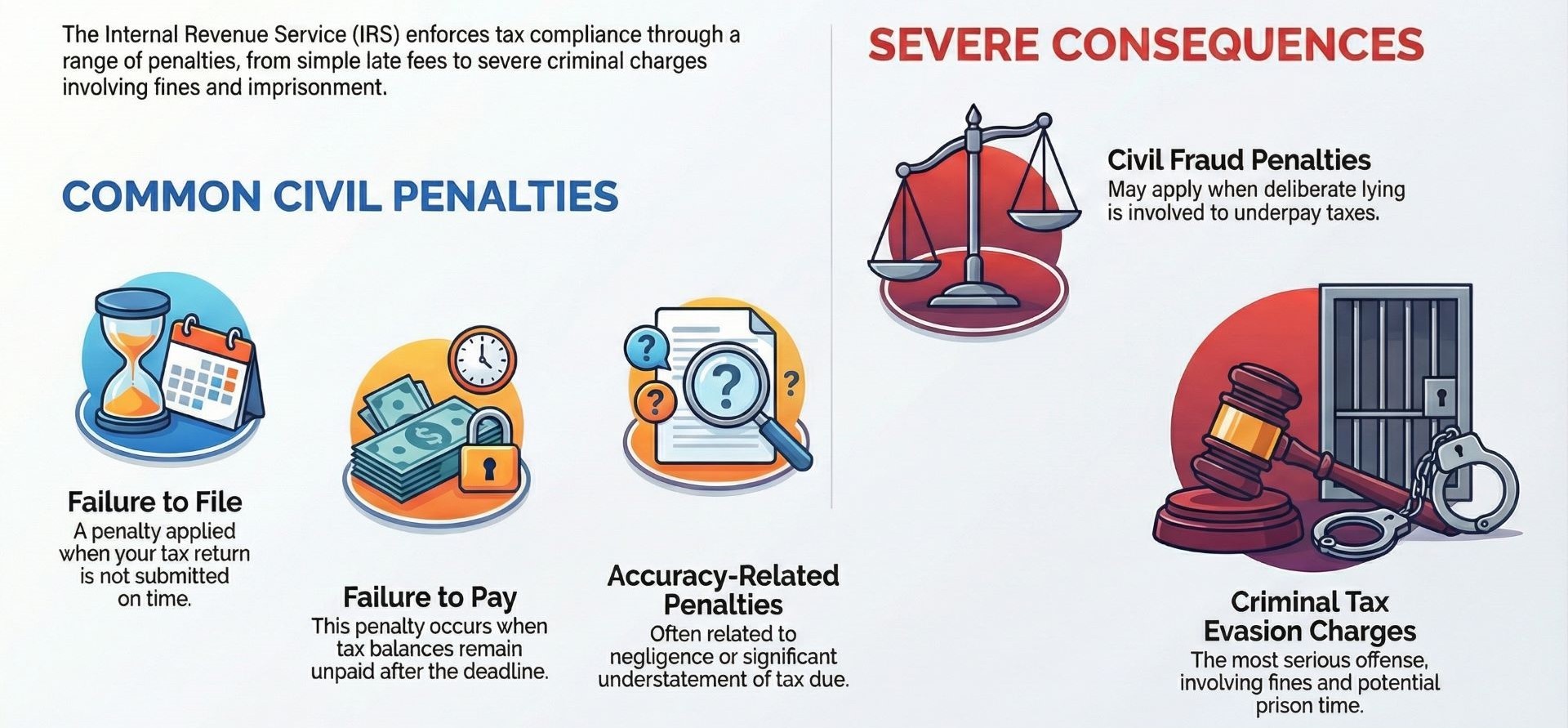
The IRS generally looks at several categories of penalties when reviewing noncompliance:
- Failure to file: It is a penalty that may be applied when a return is not submitted on time.
- Failure to pay: This penalty can occur when balances remain unpaid.
- Accuracy-related penalties: They are often related to negligence.
- Civil fraud penalties: They may apply when deliberate lying is involved for underpayment.
- Criminal tax evasion charges: This may involve fines, along with potential prison time.
When intent is established, the person may incur heavy fines, which can be higher for corporations, along with possible incarceration.
How Do Tax Evasion Consequences Affect Small Businesses
The effects can go beyond fines for small business owners, particularly in the service sector. Enforcement proceedings can result in cash flow interruptions, extended IRS communication, and reputational strain.
In Texas, we commonly see contractors, consultants, and oil-and-gas service providers facing challenges because their income streams vary month to month. And when they do not pay much attention to the bookkeeping, a gap may be established in their numbers. And over time, unresolved issues may increase exposure to enforcement actions or penalties if intent is inferred.
The U.S. Sentencing Commission also reports that hundreds of tax fraud cases that occur each year demonstrate the types of situations in which serious penalties or possible jail time may be applied when intentional noncompliance is demonstrated.
How May Intent Influence IRS Enforcement Decisions
The IRS may typically distinguish between:
- Honest mistakes
- Negligence
- Willful attempt
When will is found behind the act, tax evasion penalties may increase sharply. This is why we always tell our clients to keep up with books, because consistent records may help support clearer documentation if questions arise. Further, clear records may also help demonstrate that discrepancies were unintentional, especially when corrected proactively.
For support in bookkeeping, many business owners may also consider coordinating with tax planning Houston services, as it may highlight areas that may need attention.
A Case Study of Our Client
One of our clients is a service company owner in Houston who manages invoices by hand. Some cash receipts are not regularly documented over a number of years. The gaps appear a little at first. Later, when an inspection is initiated by inconsistent 1099 reporting, the trend becomes more apparent.
Outcomes in situations like this depend on a range of factors, including documentation, reporting patterns, and how the IRS interprets intent. Unresolved patterns can increase the likelihood of tax evasion penalties if intent is assumed, even if not every case results in enforcement.
How Accurate Tax Preparation May Support Clearer Reporting
Yes, accurate and timely filing may help support clearer communication with the IRS. Many business owners also consider a professional business tax preparation service that may assist them in understanding general IRS guidelines to prepare for the tax season in a better way.
Why Financial Reporting Matters in Tax Issues
Remembering every transaction in detail is not possible. And especially when the business expands its revenue streams, the grip on numbers may loosen. This is where taking help from a financial reporting and analysis service may come as a good idea. It may offer assistance in keeping books updated in a timely manner, which can support clearer financial visibility.
Common Compliance Practices the IRS Looks For
The IRS commonly evaluates the following factors when reviewing compliance:
- Filing returns on time.
- Reporting all income sources clearly.
- Maintaining records according to reported figures.
- Addressing errors proactively.
- Communicating with the IRS if notices are received.
FAQs About Tax Evasion Penalties
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the IRS 7-year rule?
It says that refund claims for bad debt deductions or losses from worthless securities may be filed with the IRS within seven years after the original return’s due date.
Does the IRS forgive tax debt after 10 years?
Yes, the IRS typically has ten years to recover assessed tax liability. The leftover amount is usually written off under the statute of limitations after that time.
What is the 27-month rule for the IRS?
It says that organizations seeking tax-exempt status often need to submit their exemption application within 27 months after establishment.
Are tax evasion penalties the same as tax fraud penalties?
Yes, they are related. Penalties for tax evasion vary depending on the facts, purpose, and whether the case is handled civilly or criminally. Tax evasion is a type of tax fraud.
Final Thoughts
Understanding tax evasion penalties is all about having clarity. When you understand how the IRS system evaluates, the reporting process may feel more manageable.
Meanwhile, if you are looking for general education around tax planning or financial reporting in Texas, you may find support with Dabney Tax & Accounting Services. We are a team of experienced CPAs who are aware of local Texas rules and offer guidance to businesses that may assist them in navigating the filing process in a structured way.



